
By dividing the target profit plus fixed costs ($100,000 + $80,000) by the contribution margin per unit ($200), we find that Adam needs to sell 900 units. To calculate the required sales volume, we can adapt the formula used for break-even analysis. By setting the profit equal to $100,000, we can rearrange the formula to find the necessary sales volume.
The Importance of Target Profit in Business
- In this way, the target profit acts as a guiding factor in decisions beyond pricing, influencing choices that impact the company’s overall financial health and strategic direction.
- For example, if a company is considering a price increase, the analysis can show how many fewer units need to be sold to maintain the same profit level.
- This equilibrium is achieved when the unit contribution margin, which is the profit contribution per unit sold, multiplied by the quantity sold, equals the fixed cost.
- Let’s say a business has annual fixed costs of £65,000, variable costs per unit of £10 and a selling price per unit of £30.
- For instance, a business can set a dollar amount to achieve through increased sales.
Break-even analysis is a fundamental tool for businesses to understand the point at which total revenues equal total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. This analysis provides valuable insights into the financial health of a company and helps in making informed decisions about pricing, production levels, and cost management. Once the process of using the profit target formula has been completed, the results can be used as the basis for starting the financial projections for the business plan. learn bookkeping and accounting online for free With the concept of the break-even point firmly in place, let’s move on to exploring a scenario where Adam Electronics seeks to earn a target profit of $100,000. This scenario showcases the essence of target profit analysis, a tool that assists businesses in determining the necessary sales volume to achieve their desired profit levels. In this exploration of target profit analysis, we will delve into the intricacies of this financial tool, focusing on its application within a real-world scenario.
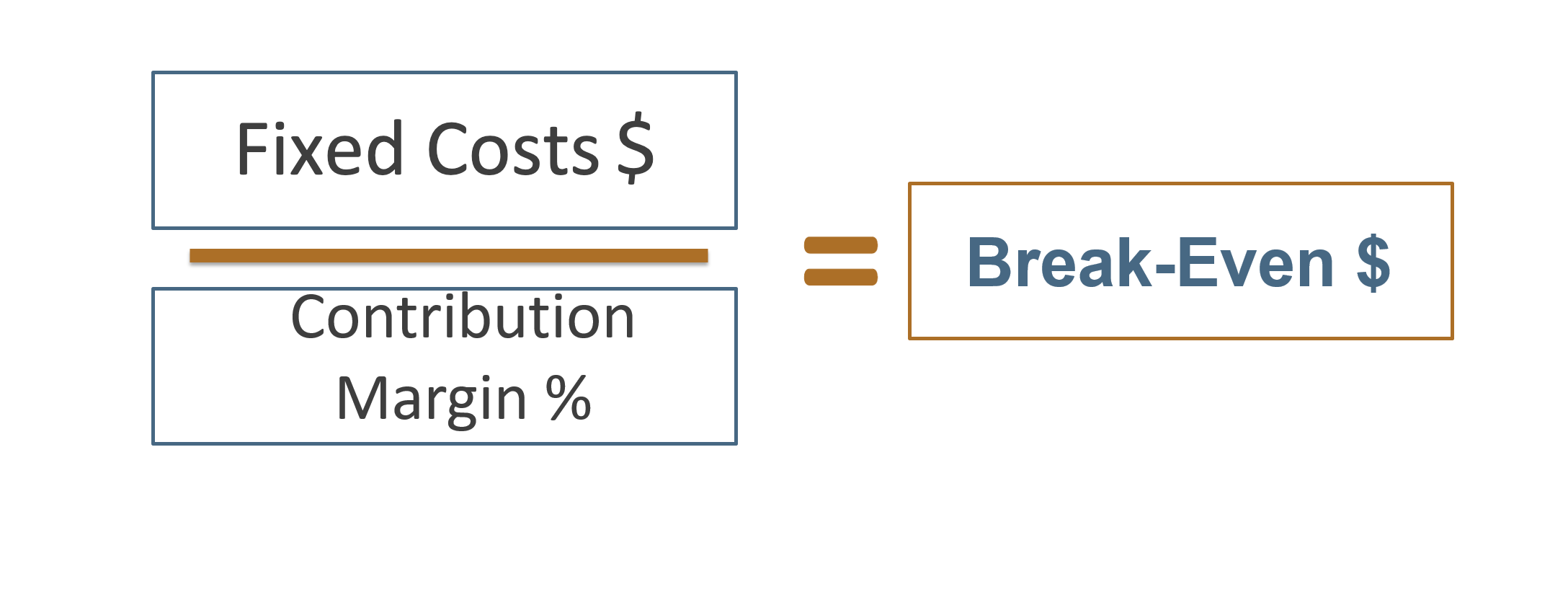
Contribution margin method for target profit:
Taking $100,000 and dividing it by the contribution margin ratio of 40%, this calculation yields a sales figure of $250,000. For example, if the target profit level is 7,000, fixed costs 36,200, and the gross margin percentage is 60%, then the revenue needed to achieve the target profit is given as follows. The second method is to first calculate the contribution margin and then set a target profit.
Target Sales Volume Formula
Any adjustments for the variance in the actual and projected results can be adjusted in this final step as well. In previous pages of this chapter, we have focused mainly on the break-even point. However, the core objective of every business is not just to break even, but to earn a decent amount of profit.
Example 4 – Variance Costs Unknown
Now, let’s check your understanding of calculating the target profit point. For example, think of a restaurant chain that has set a target profit for each location based on factors like foot traffic and operating costs. If the target profit suggests a need for increased production, the company can invest in additional machinery or resources to meet the demand.
One effective method for calculating target profit is the contribution margin approach. The contribution margin is the difference between sales revenue and variable costs. By determining the contribution margin per unit, businesses can estimate how many units need to be sold to cover fixed costs and achieve the target profit.
Calculating this target involves a thorough understanding of both fixed and variable costs, as well as the revenue needed to cover these expenses and generate the desired profit. Analyzing the sales mix involves examining the contribution margin of each product and understanding how shifts in sales volumes affect overall profitability. For example, if a company notices an increase in the sales of a high-margin product, it can expect an improvement in its overall profit margins.
By understanding the desired profit margin and considering the overall market, the business can lay the groundwork for sustainable growth. In this way, the target profit acts as a guiding factor in decisions beyond pricing, influencing choices that impact the company’s overall financial health and strategic direction. Target profit is an integral part of the cost-volume-profit or the CVP analysis.
As an illustration, suppose a start up manufacturing business wants to target a profit of 15,000 in its financial projections. Additionally its product sells for 15.00 and costs 6.75 to produce, and it has fixed costs of 60,000. The number of units it needs to sell to reach its profit target is as follows. In break-even point analysis article, we used equation method and contribution margin method to calculate break-even point of a company. The same formulas, with a little modification, can be used to calculate the sales both in units and in dollars to earn a target profit during a certain period of time. In the world of business and finance, the impact of taxes is a reality that companies must consider when setting target profit goals.
However, in many cases, there are several similar products manufactured in the same facility. If it is set to zero in the above equation, it will give the break-even point in terms of sales. However, many businesses fail to achieve it through this approach as they cannot control budgets.
